
LASER LENSES


LOWER & UPPER PROTECTIVE LENS
KEY FEATURES:
SIZE : 27.9*4.1, 24.9*1.5, 25.4*4.1
MATERIAL : Fused Silica ( FS)
DIAMETER TOLARENCE : +-
COATING : AR/AR @1064nm
TRANSMISSION : >99.5%
DISCRIPTION:
Fiber laser protective lenses, both lower and upper, serve vital functions in shielding sensitive optical components from damage during laser processing. Here's a breakdown of their usage and differences:
Usage: The lower protective lens is positioned closer to the workpiece or material being processed by the laser. It serves as the first line of defense against debris, splatter, and other contaminants generated during laser operations.
Function: The lower protective lens is designed to withstand direct exposure to harsh environmental conditions such as heat, debris, and chemical residues. It helps maintain the integrity and longevity of the more delicate optical components located further up the laser system.
Usage: The upper protective lens is situated closer to the laser source or optical components within the fiber laser system. It provides additional protection for critical optical elements such as focusing lenses and mirrors and also to QBH or main quartz area of Fiber Optic cable to some extent .
Function: The upper protective lens shields these sensitive components from damage caused by back reflections, intense laser energy, and any residual debris that may pass through the lower protective lens. It helps ensure the reliability and performance of the entire laser system.
- Positioning: The lower protective lens is closer to the workpiece, while the upper protective lens is closer to the laser source.
- Purpose: The lower protective lens primarily guards against external contaminants and debris, while the upper protective lens protects internal optical components from damage and degradation.
- Exposure: The lower protective lens is more exposed to the laser processing environment, whereas the upper protective lens is shielded within the laser system.
Choosing the appropriate protective lenses depends on factors such as the specific laser processing application, power levels, and environmental conditions. Both raytools original laser lenses lower and upper protective lenses are essential for ensuring the reliability, longevity, and safety of fiber laser systems.
ESSELL provides Raytools original laser lenses for the fiber laser cutting machine and for the best performance and efficiency of the machine and machine head. As ESSELL provides original Raytool Head like BM110, BM111, BM04K, BM114....... thus, one can contact us for Raytools original laser lenses.


FIBER LASER COLLIMATIC LENS
KEY FEATURES:
SIZE : Normally D28 , D32 and D37 depending on Laser Head model used with machine.
MATERIAL : Fused Silica ( FS)
DIAMETER TOELRANCE :+-0.2nm
COATING : AR/AR @1064nm
TRANSMISSION : >99.8%
High purity Fused Silica, High Temperature Resistance
DISCRIPTION:
Fiber laser collimating lenses, both concave and convex, serve crucial roles in directing and focusing laser beams within fiber optic systems. Here's a breakdown of their usage and differences:
Usage: Concave collimating lenses are primarily used to diverge or spread out laser beams. They are often employed at the output end of a fiber optic system to expand the beam diameter.
Function: When a laser beam passes through a concave lens, it diverges, spreading out over a wider area. This can be beneficial for applications such as laser cutting or welding, where a wider beam diameter is advantageous.
Usage: Convex collimating lenses are utilized to converge or focus laser beams. They are typically placed at the input end of a fiber optic system to focus the beam to a smaller spot size.
Function: As a laser beam passes through a convex lens, it converges, focusing the beam to a smaller spot size. This is essential for applications like laser engraving or drilling, where precision and focused energy are required.
- Direction of Beam: Concave lenses diverge the beam, while convex lenses converge it.
- Application: Concave lenses are used for spreading or diverging beams, while convex lenses are used for focusing or converging them.
- Effect on Beam Diameter: Concave lenses increase the beam diameter, while convex lenses decrease it.
- Spot Size: Convex lenses produce a smaller spot size compared to concave lenses.
Understanding the specific requirements of an application is crucial for selecting the appropriate raytools original laser lenses type of collimating lens to achieve desired beam characteristics and performance.
ESSELL provides Raytools original laser lenses for the fiber laser cutting machine and for the best performance and efficiency of the machine and machine head. As ESSELL provides original Raytool Head like BM110, BM111, BM04K, BM114....... thus, one can contact us for Raytools original laser lenses.




FOCUS CONVEX & CONCAVE LENS
KEY FEATURES:
SIZE : D28 ,D32 AND D37 Depending on laser head used with Laser Cutting Machine
MATERIAL : Fused Silica ( FS)
DIAMETER TOLARENCE : +-0.2 nm
COATING : AR/AR @1064nm
TRANSMISSION : >99.8%
High purity Fused Silica, High Temperature Resistance
DISCRIPTION:
Fiber laser focus lenses, both convex and concave, play essential roles in manipulating the focal point and spot size of laser beams within fiber optic systems. Here's how they're used and their differences:
Usage: Concave focus lenses are employed to diverge or spread out laser beams. They are often utilized at the output end of a fiber optic system to expand the beam diameter.
Function: When a laser beam passes through a concave lens, it diverges, spreading out over a wider area. This can be advantageous for applications such as laser marking or surface treatment, where a larger spot size is beneficial.
Usage: Convex focus lenses are used to converge or focus laser beams. They are typically positioned at the output end of a fiber optic system to focus the beam to a smaller spot size.
Function: As a laser beam passes through a convex lens, it converges, focusing the beam to a smaller spot size. This is critical for applications like laser cutting or welding, where precise focusing and high energy density are required.
- Direction of Beam Manipulation: Concave lenses diverge the beam, while convex lenses converge it.
- Application: Concave lenses are used for spreading or diverging beams, while convex lenses are used for focusing or converging them.
- Effect on Spot Size: Convex lenses produce a smaller spot size compared to concave lenses.
- Focal Length: Concave lenses have a negative focal length, while convex lenses have a positive focal length.
Selecting the appropriate type of focus lens depends on the specific requirements of the application, including desired spot size, working distance, and laser power. Understanding these factors is crucial for achieving optimal performance and efficiency in laser processing tasks.
ESSELL provides Raytools original laser lenses for the fiber laser cutting machine and for the best performance and efficiency of the machine and machine head. As ESSELL provides original Raytool Head like BM110, BM111, BM04K, BM114....... thus, one can contact us for Raytools original laser lenses.


SINGLE & DOUBLE LAYER NOZZLES
KEY FEATURES:
- Consumable/Replacement Parts for Raytools or any other Fiber Laser cutting Head
- Double Layers with Chrome Plating
- Diameter: 28mm/32 mm , Height: 15mm, M14
- Optional Caliber: 0.8-6mm
- Used for Fiber Laser Cutting Head
DISCRIPTION:
Fiber laser nozzles, whether single or double-layered, play critical roles in laser cutting and welding applications. Here's a breakdown of their usage and differences:
Usage: Single-layer nozzles are commonly used in laser cutting and welding processes where precision and high-speed operation are required. Typical metals where this single nozzle is used is SS, Brass , GI , Copper etc
Function: These nozzles typically have a single opening through which the laser beam is directed onto the workpiece. They provide efficient gas delivery (such as oxygen or nitrogen) to the cutting or welding zone, helping to maintain optimal process conditions and assist in material removal or fusion.
Usage: Double-layer nozzles are utilized in laser cutting applications that require enhanced cooling and protection of the optics. The Typical material where this nozzle is mainly used is Mild Steel / Carbon Steel
Function: These nozzles consist of two layers: an inner layer through which the laser beam passes, and an outer layer that directs assist gas around the beam path. The dual-layer design helps to isolate the laser beam from the surrounding atmosphere, reducing the risk of contamination and improving cutting performance, especially when processing materials prone to oxidation or contamination.
- Design: Single-layer nozzles have a simpler design with a single opening, while double-layer nozzles have an additional outer layer for gas delivery.
- Application: Single-layer nozzles are suitable for general-purpose laser cutting and welding, while double-layer nozzles are preferred for applications requiring enhanced cooling and protection of optical components. The typical metals where this single nozzle is used are SS , Brass , GI , Copper etc
- Performance: Double-layer nozzles offer improved gas flow dynamics and better protection of the laser optics compared to single-layer nozzles.
- Material Compatibility: Double-layer nozzles are often used for cutting materials sensitive to oxidation or contamination, while single-layer nozzles are suitable for a wide range of materials. Its use mainly for Carbon Steel or Mild Steel
Selecting the appropriate type of nozzle depends on factors such as the specific laser application, material being processed, desired cutting quality, and the level of protection required for the optical components. Both single and double-layer nozzles play crucial roles in optimizing laser processing performance and efficiency.



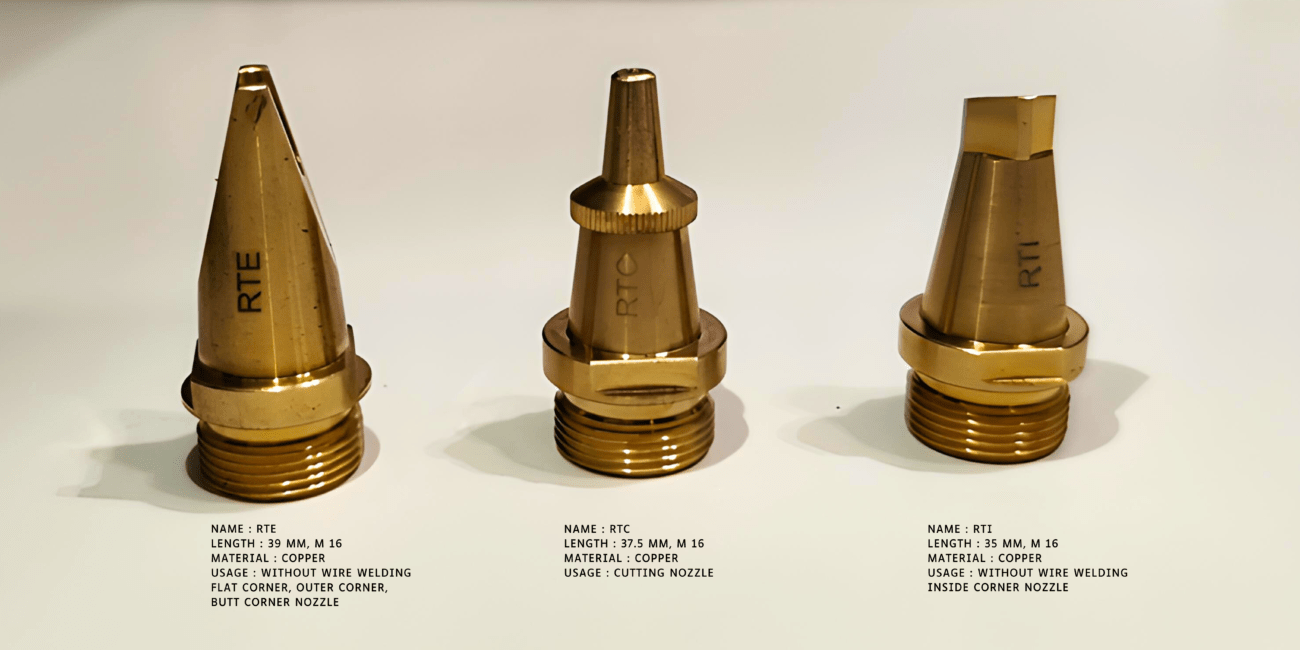
WELDING NOZZLES
KEY FEATURES:
- Consumable/Replacement Parts for Raytools Fiber Laser Welding Head
- Nozzles are different in size and share based on application like Laser Welding , Laser Cleaning , Laser Cutting etc
DISCRIPTION:
Fiber laser welding nozzles, with and without wire feed, are essential components in laser welding processes. Here's a breakup of their usage and descriptions:
Usage: These types of nozzles are commonly used in laser welding applications where a filler wire is not required or where the wire is fed separately.
Description: Nozzles without wire feed typically have a streamlined design with a single or multiple openings through which the laser beam is directed onto the workpiece. They focus the laser energy onto the weld joint, providing efficient shielding gas delivery to protect the weld pool from atmospheric contamination. These nozzles are ideal for welding thin materials or performing autogenous (wire-free) welds.
Usage: Nozzles with wire feed are utilized in laser welding processes where a filler wire is integrated directly into the welding nozzle assembly.
Description: These nozzles have a more complex design compared to those without wire feed. They typically feature a dual-channel system—one for the laser beam delivery and the other for feeding the filler wire. The wire feed is synchronized with the laser beam, ensuring precise control over the deposition of the filler material. This allows for the welding of thicker materials or the creation of stronger weld joints by introducing additional material into the weld pool.
- Wire Integration: Nozzles without wire feed do not incorporate a wire feeding mechanism, while nozzles with wire feed integrate a system for feeding filler wire directly into the weld zone.
- Application: Nozzles without wire feed are suitable for autogenous welding or applications where a separate wire feeding system is employed. Nozzles with wire feed are used when precise control over filler material deposition is required.
- Complexity: Nozzles with wire feed have a more complex design due to the integration of the wire feeding mechanism.
- Welding Capabilities: Nozzles with wire feed enable the welding of thicker materials and the creation of stronger weld joints by introducing additional filler material.
Choosing the appropriate type of welding nozzle depends on factors such as the specific welding application, material type and thickness, desired weld quality, and the availability of wire feeding equipment. Both types of nozzles play crucial roles in achieving precise and efficient laser welding results.
OUR GALLERY
OUR PRODUCTS




Professional Fiber Laser Pipe Cutting Machine






Choosing the Right Laser Lenses From Essell
With more than ten years of experience in laser technology, ESSELL distinguishes itself as a leading engineering solution provider in the quickly changing manufacturing sector. Because of our vast experience, we are able to supply top-notch equipment that are efficient and precisely constructed to meet a range of industrial needs. Our products, which range from advanced pipe cutting machines to laser sheet cutting machines, are designed to satisfy the various demands of our customers.
Our area of expertise at ESSELL is producing state-of-the-art laser cutting equipment and associated technologies. Automatic laser cutting machines, laser steel cutting machines, and machines made especially for welding and marking applications are among our product offerings. We take great satisfaction in our ability to combine cutting-edge technology with intuitive designs, guaranteeing that our machines operate at their best. The laser sheet cutting machine is one of our most notable products. This machine has been painstakingly designed to quickly and precisely handle a range of sheet materials. It focuses the laser beam using premium laser lenses and laser light lenses, enabling precise cuts and elaborate designs that satisfy the highest quality standards. Our dedication to using top-notch laser machine lenses guarantees that each cut is precise and reliable, increasing efficiency throughout your business.
Innovative and Cutting-Edge Technology
Our work is centered on innovation. We are aware that in the highly competitive world of today, manufacturers need equipment that can both satisfy their present demands and grow with them to meet new ones. To improve the functionality of our CNC machines and laser systems, our engineering staff is always investigating new technologies. Our pipe cutting machines have completely changed how companies handle metal manufacturing. These machines offer unmatched adaptability and efficiency because they are made to handle pipes of different diameters and thicknesses. Fast and accurate cuts are made possible by the incorporation of cutting-edge laser technology, which minimizes material waste and improves production cycles.
How Laser Lenses Work: The Science Behind Precision Vision
Quality is our first concern at ESSELL. We carefully choose parts and materials to guarantee that each machine we build satisfies exacting quality requirements. Our laser machine lens systems are put through a thorough testing process to ensure dependability, performance, and longevity. Furthermore, we think that establishing enduring bonds with our clients is important. Our committed support staff is on hand at all times to help with installation, upkeep, and troubleshooting. In order to maximize your investment in laser technology, we provide thorough training programs that guarantee your team can confidently handle our machines.
Why Should You Choose Essell As A Laser Machine Manufacturer?
To sum up, ESSELL is your progress partner and more than just an engineering solutions provider. With more than a decade of experience in the laser welding machine field, we are dedicated to providing creative, high-performing solutions that boost production and efficiency in your manufacturing operations. ESSELL has the resources and experience to satisfy your needs, whether you're searching for sophisticated CNC machines, pipe cutting machines, or laser cutting equipment. To find out more about how we can assist


